Table of Contents
As the world becomes fully connected, the value of 5G becomes apparent. One of the most important, yet most ignored, features of data transmission efficiency is transport block size. Knowing the ins and outs of transport block size makes a difference in fully optimizing performance within a network. With rising requests for speed and demanding low latency, the need for an understanding of transport block size is more important than ever. Read along as this blog outlines the most important aspects and offers solutions for increasing 5G NR network data throughput.
How is Transport Block Size Determined in 5G NR?
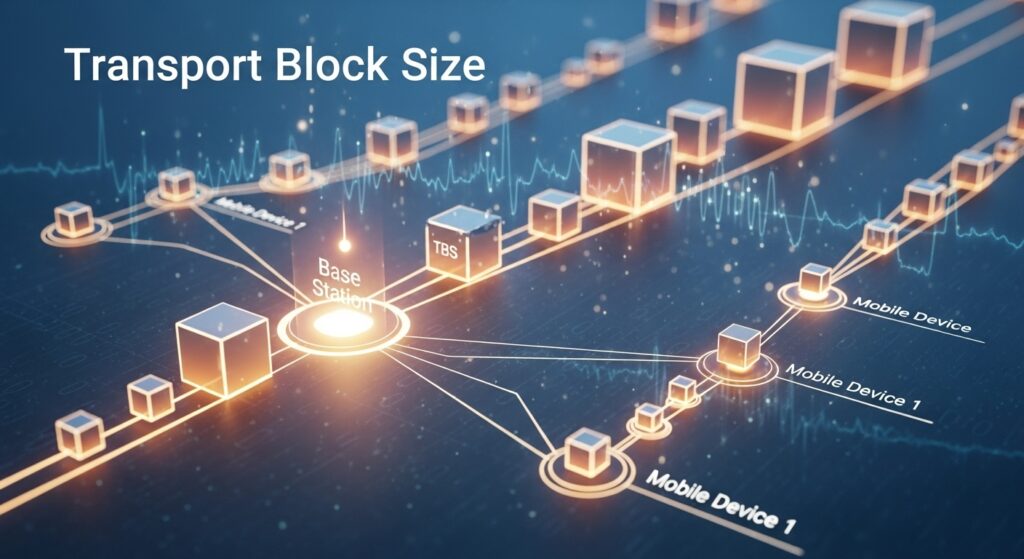
Transport block sizes in 5G NR are determined by physical layer standards, which encompass different modulation schemes and coding rates. The maximum transport block size is conditional on the specific service being used. Whether it is enhanced mobile broadband, ultra-reliable low-latency communications, or massive machine-type communications, each service has distinct characteristics that affect the efficiency of data packing.
Transport block size also depends on the channel condition, which refers to the real-time condition of the network, like signal strength and interference within the currently active range. The capabilities of user equipment are also crucial in deciding the transport block size. Different devices have different optimal sizes that network equipment needs to account for when tailoring its configuration to the device.
Factors Affecting Transport Block Size in 5G NR
At least 3 key components should be considered when determining 5G NR transport block size. One key component is the level of dispersion in the modulation scheme. The use of advanced modulation schemes like 256 QAM would justify the need to capture higher-order dispersion in the modulation scheme, as more bits per transmission symbol can be recorded. 256 QAM would, however, entail more elaborate provisions of signal conditions. Channel condition provides the next rationale for block size determination.
If the signal condition is strong, large block sizes can be used. A weaker signal condition, however, requires the use of smaller block sizes to increase the probability of successful transmission. Third is the coding rate/rates derived during the encoding of data for transmission. Low coding rate means that there is better error protection for the signal; hence, the block size can be smaller, but the data capacity becomes limited.
The last factor is the designed provisions of the user equipment and network layouts. Relative to the range of devices and varying environments, transport blocks should be roughly sized for high efficiency. These provisions maintain 5G network reliability.
Benefits of Optimizing Transport Block Size
Optimizing transport block size is critical to improving 5G NR network data throughput. Because of the transport block settings, operators gain substantial improvements in spectral efficiency, translating to enhanced throughput without increases in bandwidth. Optimized transport blocks reduce system latency. Consequently, transport blocks are able to address user latency during real-time applications such as video streaming and online gaming.
Optimized transport blocks enhance network reliability. Properly configured transport blocks minimize packet loss and unplanned service interruptions. Optimizing transport blocks also improves resource discord to network slices and improves Cross-Layer disposal. This helps telecom operators in resource allocation to balance between multiple resource strips and user slices. Optimized transport blocks reduce energy consumption during signal processing, thereby decreasing unnecessary power loss and minimizing the number of retransmissions that are needed due to error bursts.
Techniques for Optimizing Transport Block Size in 5G NR
Several techniques can be used to adjust the transport block size in 5G NR. One of the most effective techniques is adaptive modulation and coding (AMC). Networks can increase the data throughput and decrease the error rate by dynamically modifying the modulation scheme with the varying channel conditions. Scheduling algorithms can be optimized in other methods. Advanced resource allocation techniques divide and distribute the network resources so that each user optimally meets their specific block transport size requirements.
The use of seamless hybrid automatic repeat requests (HARQ) techniques is also vital. HARQ increases the reliability of the transmissions without significantly increasing the transport block size by combining error detection and retransmission. Resource management can also be improved through network slicing by segregating traffic according to the specific requirements of each application. This permits the differential allocation of bandwidth to support low-latency applications. These methods will need to constantly evolve and adapt to changes in user behavior based on the overall network performance and user demand.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Optimal Transport Block Sizes
Telecom operators around the world have started to embrace optimized transport block sizes, yielding impressive results. One notable case is in South Korea, where a major carrier adjusted its transport block size based on real-time traffic demands. By analyzing user behavior and adjusting parameters dynamically, they achieved a 30% increase in data throughput during peak hours. This adaptability allowed them to serve more customers without compromising quality.
In Europe, another operator employed advanced algorithms for predictive analytics. Their focus was on optimizing block sizes according to varying network conditions. The outcome? A remarkable reduction in latency and improved user experiences across urban areas. These examples demonstrate that tailored approaches to transport block sizing can significantly impact performance metrics—ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction and retention rates in the competitive telecom landscape.
Conclusion: transport block size
The size of a transport block greatly influences the effectiveness of 5G NR networks. Knowledge of the determiners and influencers of a transport block size will help operators better optimize their networks in these areas in order to maximize data throughput.
Transport block size optimization is a user experience game-changer. Various system performance enhancements tackle network efficiency from a multitude of perspectives within the optimization framework. Adaptive modulation and coding, implemented along with other buffer management techniques, greatly improves system performance excellence.
The real-world examples of optimization yield significant enhancement in speed and dependability, thus justifying the reward quotient of this optimization. Improved optimization of the value and sized block greatly benefits the user, and service equity and efficiency tremendously.
The evolving 5G will be paralleled with the evolution of techniques for optimization. The development of these techniques will be vital for wireless mobile telecommunications and technology for the foreseeable future. This is critical, as the shape of future mobile communications is built around efficient, refined, and adaptable parameters.

 fintechzoom.com US Markets Today: Stocks Surge Amid Investor Optimism
fintechzoom.com US Markets Today: Stocks Surge Amid Investor Optimism  fintechzoom com cac 40: Rises on Strong Earnings Reports
fintechzoom com cac 40: Rises on Strong Earnings Reports  fintechzoom.com nasdaq: Soars on Tech Stock Rally
fintechzoom.com nasdaq: Soars on Tech Stock Rally  fintechzoom.com economy: Rebounds on Strong Job Growth
fintechzoom.com economy: Rebounds on Strong Job Growth  fintechzoom.com bitcoin: Crashes on Market Panic
fintechzoom.com bitcoin: Crashes on Market Panic  fintechzoom.com russell 2000: Gains Reflect Market Confidence
fintechzoom.com russell 2000: Gains Reflect Market Confidence